SOCIAL MEDIA
Portuguese Medical Association's Scientific Journal
Introduction: Children and adolescents are a relevant and increasing proportion of travelers. Injuries and infectious diseases in children are safety concerns when traveling. However, data on diseases and injuries during international travels in children are not available. The aims of this study were to analyze travel-related diseases and injuries among pediatric travelers during and after international trips, to identify risk factors for travel-associated disease, and to evaluate the compliance and effectiveness of the recommendations provided in pre-travel appointments.
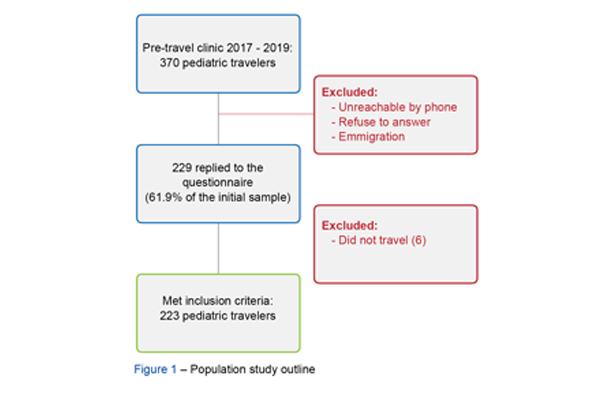
Material and Methods: We enrolled travelers aged under 18 years attending a pre-travel clinic, in a tertiary hospital (2017 - 2019); 223 of the 370 pediatric travelers attending the pre-travel clinic were included. The study was based on a questionnaire designed to address health and safety issues – vaccines and chemoprophylaxis, including side effects, the occurrence of disease or injury, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes.
Results: The median age at pre-travel evaluation was eight years; 39.7% of the travelers were adolescents, 52.5% were female. The participants traveled to 40 countries across four continents, with a median travel duration of 14.5 days. Asia was the most visited continent. Traveling was safe for 84.8%. From 34 travelers who had illness/injury, gastrointestinal symptoms were elicited in 41.2%. Sixteen (47.1%) travelers required an urgent medical appointment at the destination, and no one was hospitalized. Destinations in Africa and longer trips were significantly associated with a higher occurrence of disease/injury (p = 0.023 and p < 0.001, respectively). In a multivariable model, traveling to Africa was still significantly associated with travel-related disease/injury [OR = 2.736 (1.037 - 7.234)].
Conclusion: Disease/injury occurred in 15.2% of pediatric travelers. Even though 47.1% of the travelers required an urgent medical appointment, the developed conditions were not severe enough to warrant hospitalization. Travels to Africa and longer trips seem to be associated with a higher risk of disease and injury.