SOCIAL MEDIA
Portuguese Medical Association's Scientific Journal
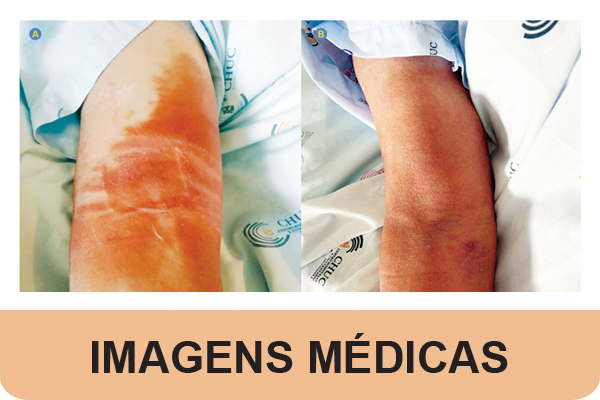
A 68-year-old female patient presented to the emergency department with dyspnea and asthenia. She had a history of heart failure induced by drug cardiotoxicity (trastuzumab). On physical examination, she displayed peripheral edema and jugular venous distension. Bloodwork revealed elevated levels of NT-proBNP (16568 pg/mL), decreased hemoglobin (10.8 g/dL), serum ferritin (41 μg/dL), and transferrin saturation (18%). We treated the patient with intravenous diuretics, levosimendan, and ferric carboxymaltose perfusion. The latter caused diffuse erythema with edema at the injection site (Fig. 1A), which was suggestive of iron skin staining (ISS), characterized by persistent hyperpigmentation (Fig 1B).