SOCIAL MEDIA
Portuguese Medical Association's Scientific Journal
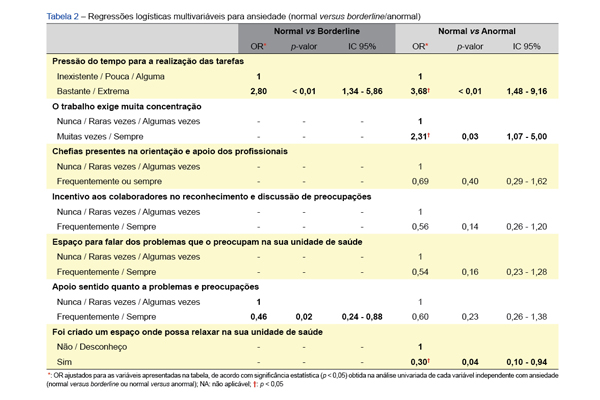
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic forced the reorganization of primary health care services. The aim of this study was to describe how the health services responded to organizational requests; how the health services involved and supported their employees; how professionals perceived their involvement in the procedures and what support was provided to them. Additions aims included assessing the levels of anxiety and depression of professionals and their association with the perceived support, availability of personal protective equipment and involvement in pandemic-related tasks.
Material and Methods: Cross-sectional, analytical study directed at professionals from three health center groups using an online questionnaire. We collected information from sociodemographic data, access to personal protective equipment, perceived support, workload and levels of anxiety and depression. Between each variable and the levels of anxiety and depression, multivariate logistic regression was applied.
Results: There were responses from 237 professionals (83.8% women; mean age 43.7 years; 43.2% physicians). Almost 60% worked with COVID-19 patients. The availability of personal protective equipment in March versus June 2020 increased (17.7% vs 55.3%). There was a risk management plan in 86% of the workplaces. A high workload (90%) and time pressure (74.6%) were identified. Physicians and nurses had a higher prevalence of depression associated with workload and fatigue (p < 0.001). Protective anxiety factors were having space to talk about problems, support in face of these problems and having a place to relax in the health unit. A lower risk of depression was found in the administrative staff group, in those who felt supported, and in those who actively participated in the contingency plans.
Conclusion: The COVID-19 pandemic led to considerable changes in the dynamics of primary health care. The time pressure to carry out tasks and the level of concentration required were associated with a higher risk of mental disease. The support felt by healthcare professionals regarding their problems and concerns and the existence of places to relax in the health units were identified as protective factors. Health promotion, the maintenance of the social contacts of healthcare professionals and their involvement in the processes should be taken into account in the organizational dynamics of the institutions.